`COVIDCurve`: COVID-19 Statistical Modeling
The purpose of this package is to provide a framework to fit age-specific infection fatality ratios (IFRs) in an epidemic that is using serologic data to estimate prevalence. The model was originally designed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic (hence the name) but is broadly applicable.
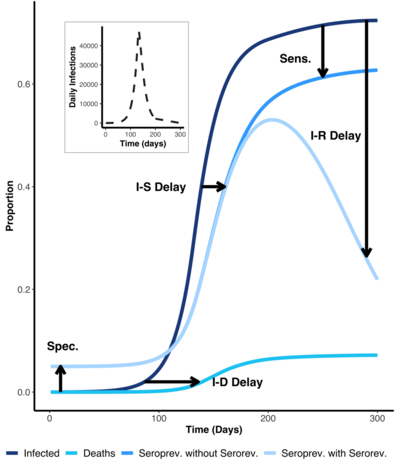
Accurate inference of the IFR based on serological data is challenging due to a number of factors that can bias estimates away from the true value, including: (1) the delay between infection and death, (2) the dynamical process of seroconversion and seroreversion, (3) potential differences in age-specific attack rates, and (4) serological test characteristics. These delay-distributions and serologic test characteristics are expected to cause both shifts in when deaths are observed as well as when and how many true infections are observed, which will then affect the IFR.
The model used in COVIDCurve can be briefly summarized as having two pieces: (1) an infection curve shape that is informed by the shape the of the observed death curve but “thrown”" backwards in time; (2) a pin or a point on the y-axis that the shape must go through (i.e. a pin to inform the area under the curve, or cumulative infections). This pin is informed by the observed serologic data, accounting for test characteristics (e.g. sensitivity and specificity) as well as the time from infection to seroconversion and seroreversion. Accounting for seroreversion, or the waning of antibodies over time that then produces a false negative test, becomes increasingly important as epidemics progress and/or as daily infections start to contract.
The IFR estimates from this model (code repo) were published as Imperial College London COVID-19 Response Team Report 341. The methodological approach for the model was published as a separate manuscript in Communications Medicine 2.
Brazeau NF, Verity R, Jenks S, Fu H, Whittaker C, Winskill P, Dorigatti I, Walker PGT, Riley S, Schnekenberg RP, Hoeltgebaum H, Mellan TA, Mishra S, Unwin HJT, Watson OJ, Cucunubá ZM, Baguelin M, Whittles L, Bhatt S, Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Okell LC.. Report 34 - COVID-19 Infection Fatality Ratio Estimates from Seroprevalence. October 2020. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-global-infectious-disease-analysis/covid-19/report-34-ifr. ↩︎
Brazeau NF, Verity R, Jenks S, Fu H, Whittaker C, Winskill P, Dorigatti I, Walker PGT, Riley S, Schnekenberg RP, Hoeltgebaum H, Mellan TA, Mishra S, Unwin HJT, Watson OJ, Cucunubá ZM, Baguelin M, Whittles L, Bhatt S, Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Okell LC. Estimating the COVID-19 infection fatality ratio accounting for seroreversion using statistical modelling. Commun Med (Lond). 2022 May 19;2:54. doi: 10.1038/s43856-022-00106-7. PMID: 35603270; PMCID: PMC9120146. ↩︎